EMR Maturity Model
Optimize and Advance EMR Use
More than 17,000 community-based family physicians, specialists and nurse practitioners in Ontario use an OntarioMD-certified EMR. Clinicians who have been using their EMRs for several years have developed the expertise to leverage many of the features of their EMR. Those who are new to EMRs are mastering the basics. To help clinicians get beyond the basics and realize the benefits an EMR has to offer, OntarioMD developed the EMR Maturity Model and the EMR Progress Assessment (EPA).
The EMR Maturity Model was designed to measure the effective use and value of an EMR. It acts as a detailed roadmap to help clinicians optimize their EMR use. The model represents the existing and potential capabilities of an EMR in the evolving digital health landscape. It represents six levels of EMR maturity across three functional areas within a practice. It uses 10 key measures to evaluate a clinician's level of EMR use.
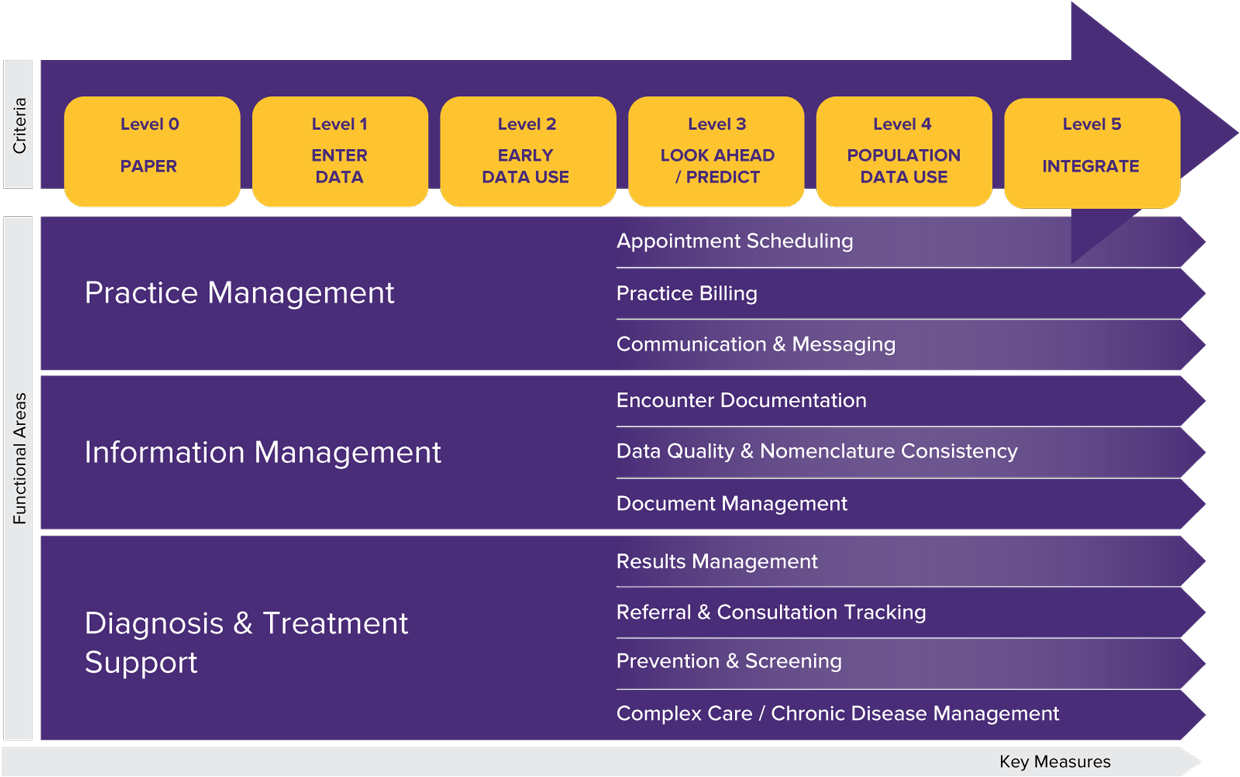
The EMR Maturity Model is a standardized way to assess EMR proficiency that is comparable to other provincial and international methods and models. It helps clinicians understand their current EMR use and determine how else they want to be using their EMR to meet practice goals.
EMR Maturity Model
| Level | Criteria | Capabilities
|
|---|
5
| Integrate | Use of portals, hubs, attachment to provincial e-health platforms sharing data from the EMR. |
| 4 | Population Data Use | Dashboarding of whole populations, acting upon the whole, performing population analysis at the practice level. |
| 3 | Look Ahead / Predict | Reminders and alerts are used at the point of care. Searches are done regularly and scheduled for review. |
| 2 | Early Data Use | Acting upon the output of episodic searches, quick entry tools, forms, calculators, etc. |
| 1 | Enter Data | Documentation occurs electronically. Progress notes, forms, and other documents are entered into the EMR. |
| 0 | Paper | Processes are primarily paper-based.
|